“Innovation is not about improving the present, but creating the future”
Advancement in smart biosensor bring healthcare closer, faster and smarter. These modern devices combine biology with advanced electronics and digital technologies to detect biological signals with high accuracy and speed. With continuous progress in biomedical engineering, smart biosensors are transforming healthcare by enabling real time health monitoring, early disease detection and personalized medical care.
What makes a smart biosensor?
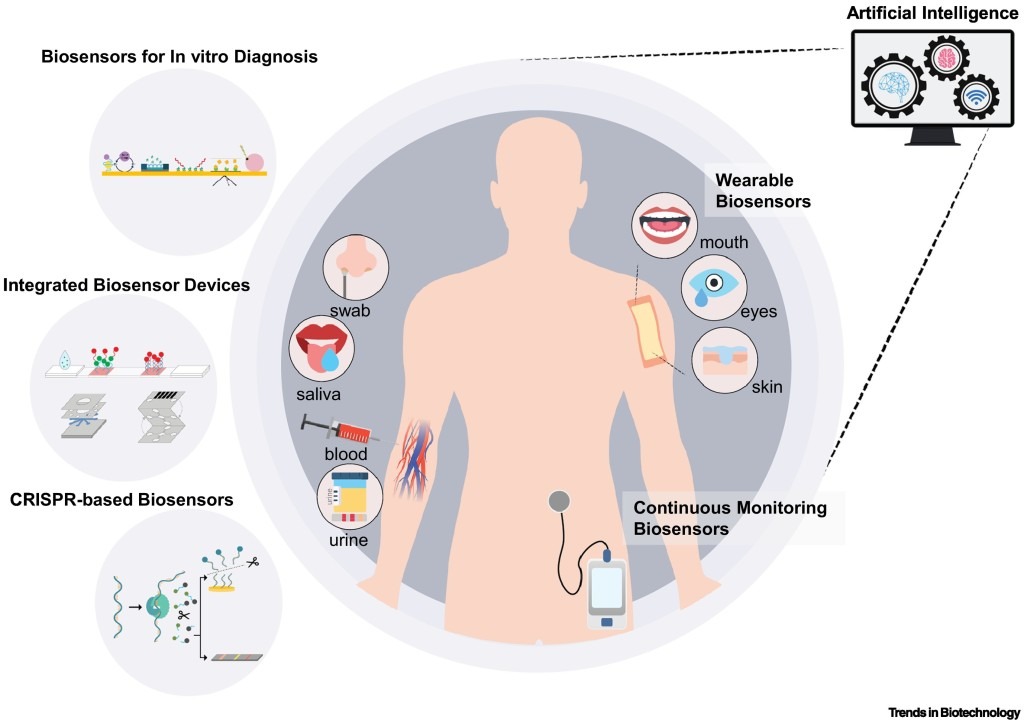
Smart biosensor incorporates:
Components
Biological recognition element (enzymes, antibodies, DNA probes)
Transducer (converts biological response to electrical signal)
Signal processing & communication unit (AI, wireless data transmission)
Technological advancement in smart biosensor
➢ Nanomaterial based biosensor
➢ AI integration
➢ Wearable and flexible biosensor
Application of advanced smart biosensor
➢ Continuous glucose monitoring
➢ Early disease detection
➢ Heart rate and blood pressure monitoring
➢ Wearable health devices
Advantages:
➢ High sensitivity and accuracy
➢ Real time continuous monitoring
➢ Portable and wearable designs
➢ Automated data processing and interpretation
➢ Connectivity with digital platforms
Disadvantages:
➢ High cost of development and manufacturing
➢ Complex design
➢ Data privacy and security issues
➢ Performance can be affected by temperature. pH and environment condition
➢ Calibration & long term stability issues
➢ Power management can be challenging for continuous monitoring
Causes and Effects of Limitations:
Causes:
➢ Complex design and costly materials
➢ Environmental sensitivity (temperature, pH, humidity)
➢ Dependence on wireless systems (data security risk)
➢ Advanced fabrication and calibration needed
Effects:
➢ High cost limits adoption
➢ Performance may vary in real conditions
➢ Risk of false readings
➢ Increased maintenance and technical support
Problem and Solution:
Problem:
➢ Expensive, sensitive to environment, requires technical expertise
➢ Risk of data breaches and unreliable readings
Solution:
➢ Use low-cost materials and simplified fabrication
➢ AI for error correction and predictive analysis
➢ Improved calibration, biocompatibility, and secure wireless systems
➢ Wearable and portable devices for real-time monitoring
Conclusion:
Smart biosensor technology is a fusion of biology, electronics, and digital technology to create devices capable of monitoring health in real time. These devices provide accurate, portable, and wearable solutions for many different uses; however, their success will depend on addressing some key challenges (cost, environmental sensitivity, and technical complexity) that currently exist. Continued research into making smart biosensors even more effective and accessible for future use in healthcare continues to be important.